In recent years, the global commercial refrigeration equipment industry is undergoing in-depth changes in technology iteration and design concepts. With the promotion of carbon neutrality goals and the diversification of consumer market demands, freezer design is gradually shifting from a single function orientation to a comprehensive model that emphasizes high efficiency, energy saving, intelligent integration, and user experience.
According to statistics from the International Energy Agency (IEA), in 2020, the energy consumption of global refrigeration equipment accounted for 10% of electricity consumption, prompting the industry to accelerate the research and development of low-GWP (global warming potential) refrigerants and variable frequency compressor technologies.
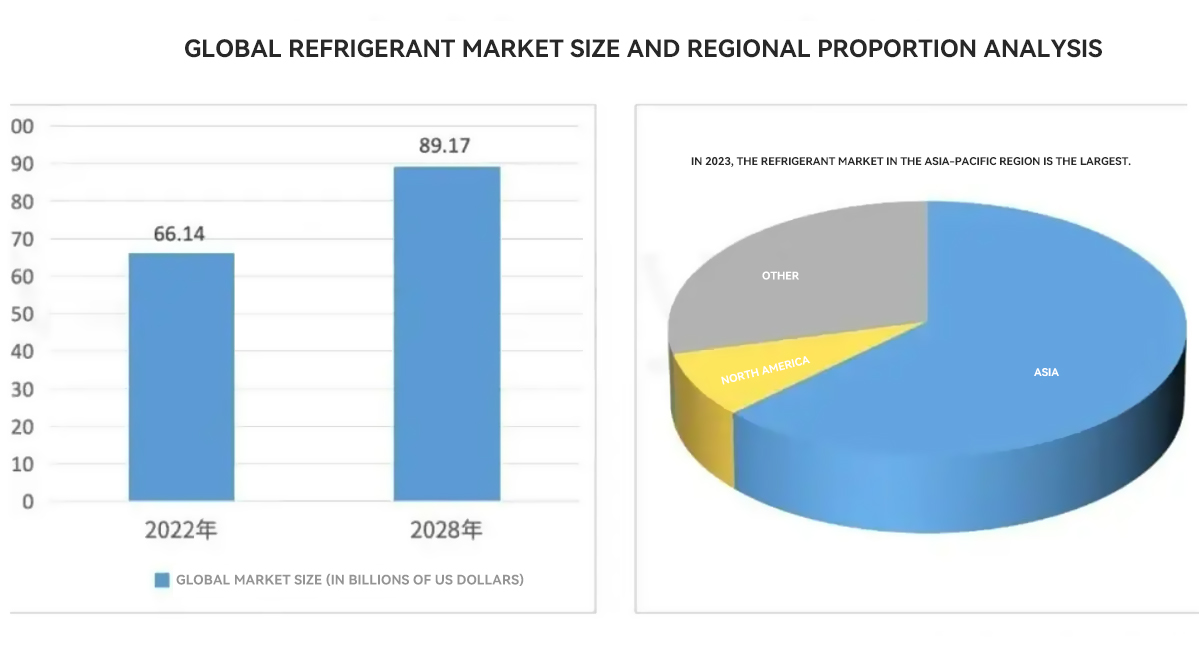
At the same time, the rise of e-commerce and new retail scenarios has promoted freezer design to pay more attention to space utilization and scene adaptability. For example, the growth of segmented categories such as convenience store multi-temperature zone freezers and unmanned retail cabinets is significant. Market research institution Technavio predicts that the global commercial refrigeration equipment market size will increase by 12.6% from 2023 to 2027, and the demand in the Asia-Pacific region accounts for more than 40%, becoming the core growth engine.
The current commercial freezer design presents three core highlights:
1. Upgrade of environmental protection performance
The proportion of freezers using natural refrigerants (such as R290, CO₂) is increasing year by year. The tightening of the EU F-Gas regulations has accelerated the popularization of hydrocarbon refrigeration technology. In addition, the foaming layer material has shifted from traditional HCFC to low environmental load solutions such as cyclopentane, and the insulation performance has increased by 15%-20%.
2. Durability and ease of maintenance
The cabinet structure tends to be modular design. Stainless steel inner liners, anti-rust coatings and antibacterial panels have become standard configurations. Some brands have launched a 10-year warranty commitment to strengthen the durability label.
3. Fashionable appearance
Elements such as matte metal texture, curved glass doors, and embedded LED light strips are widely used. High-end models even introduce customizable color film panels to meet the visual needs of scenes such as coffee shops and boutique supermarkets.
Future direction in 2026 – deepening of intelligence and sustainability
By 2026, commercial freezer design will revolve around AIoT (Artificial Intelligence Internet of Things) and full life cycle low carbonization:
Intelligent temperature control system: Through sensors to monitor inventory and energy consumption in real time, combined with AI algorithms to dynamically adjust the operating mode, it is expected to reduce energy consumption by 20%-30%;
Material circular economy: Detachable structure design, bio-based plastic cabinets and the application of recyclable foaming agents will become the mainstream. Some enterprises explore the “rental instead of sales” model to extend the service life of equipment;
Scene customization: For emerging needs such as pre-made dishes and pharmaceutical cold chains, develop multi-functional freezers with dual control of temperature and humidity and multi-zone independent management.
Precautions:
Energy efficiency compliance risk: Energy efficiency standards in various countries (such as the US Energy Star and China’s GB standard) are continuously updated. Attention needs to be paid to parameters such as COP (coefficient of performance) and APF (annual energy efficiency ratio);
Environmental protection regulatory barriers: The EU carbon tariff (CBAM) may impose fees on high-carbon footprint refrigeration equipment. The supply chain needs to plan low-carbon alternative solutions in advance;
User experience pain points: Details such as noise control (needs to be lower than 45dB) and the airtightness of door seals affect terminal procurement decisions.
In the future, it is necessary to pay attention to the balance between investment cost and long-term energy-saving benefits. The price of high-efficiency models is 30%-50% higher than that of traditional models. It is necessary to persuade customers through life cycle cost analysis. At the same time, intelligence and data security. The ownership of temperature control data of networked freezers and privacy protection have triggered industry discussions.
Post time: Apr-10-2025 Views: